Company Information
Ask for more detail from the seller
Contact SupplierDesalination -A Promise for the Future
As per a projection, by 2025 there will be severe water shortage in over 50 countries, affecting 2.8 billion people - 35% of world’s projected population.
Desalination is a process that removes dissolved minerals (including but not limited to salt) from sea water, brackish water, or treated wastewater. A number of technologies have been developed for desalination, including reverse osmosis (RO), distillation, electro-dialysis and vacuum freezing. Two of these technologies; RO and distillation are being considered for their economical viability by municipalities, water districts, and private companies for development of sea water desalination. These methods are described below.
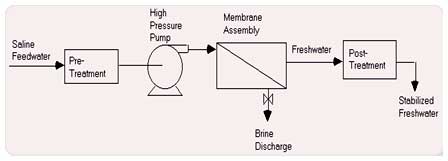
Reverse Osmosis (RO)
In RO, feed water is pumped at high pressure through permeable membranes, separating salts from the water (Figure 1). Feed water is pre-treated to remove particles that would clog the membranes. The quality of the water produced depends on the pressure, the concentration of salts in the feed water and the salt permeation constant of the membranes. Product water quality can be improved by adding a second pass (Module) of membranes, whereby product water from the first pass (Module) is fed to the second pass (Module).
Distillation
In the distillation process, feed water is heated and then evaporated to separate out dissolved minerals. The most common methods of distillation include Multi-Stage Flash (MSF), Multiple Effect Distillation (MED), and Vapor Compression (VC).
In MSF, the feed water is heated and the pressure is lowered, so the water "flashes" into steam. This process constitutes one stage of a number of stages in series, each of which is at a lower pressure. In MED, the feed water passes through a number of evaporators in series. Vapor from one series is subsequently used to evaporate water in the next series. The VC process involves evaporating the feed water, compressing the vapor, and then using the heated compressed vapor as a heat source to evaporate additional feed water. Some distillation plants are a hybrid of more than one desalination technologies. The waste product from these processes is a solution with high salt concentration.
Input Water (Feed water)
Desalination plants may use sea water (directly from the ocean through offshore intakes and pipelines or from wells located on the beach or sea floor), brackish ground water, or reclaimed water as feed water. Since brackish water has lower salt concentration, the cost of desalting brackish water is generally less than the cost of desalting sea water. Intake pipes for desalination plants should be located away from sewage treatment plant outfalls to prevent intake of discharged effluent. If sewage treatment discharges or other types of pollutants are included in the intake, however, the pre and post-treatment processes should remove the pollutants.
Product Water
Distillation plants produce high-quality product water that ranges from 1.0 to 50 ppm tds, while RO plants produce product water that ranges from 10 to 500 ppm tds. (The recommended California drinking water standard for maximum tds is 500 mg/L, which is equivalent to 500 ppm.) In desalination plants that produce water for domestic use, post-treatment processes are often employed to ensure that product water meets the health standards for drinking water as well as recommended aesthetic and anti-corrosive standards.
Desalination product water may be used in its pure form (e.g., for make-up water in power plant boilers) or it may be mixed with less pure water and used for drinking water, irrigation, or other uses. The desalinated product water is usually more pure than drinking water standards, so when product water is intended for municipal use, it may be mixed with water that contains higher levels of total dissolved solids. Pure desalination water is highly acidic and is thus corrosive to pipes, so it has to be mixed with other sources of water that are piped onsite or else adjusted for pH, hardness, and alkalinity before being piped offsite.
Product Water Recovery
The product water recovery relative to input water flow is 15 to 50% for most sea water desalination plants. For every 100 gallons of sea water, 15 to 50 gallons of pure water would be produced along with brine water containing dissolved solids. A desalination plant's recovery varies, in part because the particulars of plant operations depend on site-specific conditions. In several locations in California, pilot projects are being proposed to test plant operations before full-scale projects are built.
Pre-treatment Processes
Pre-treatment processes are needed to remove substances that would interfere with the desalting process. Algae and bacteria can grow in both RO and distillation plants, so a biocide (usually less than 1 mg/L chlorine) is required to clean the system. Some RO membranes cannot tolerate chlorine, so dechlorination techniques are required. Ozone or ultraviolet light may also be used to remove marine organisms. If ozone is used, it must be removed with chemicals before reaching the membranes. An RO technology has been developed recently that does not require chemical pre-treatment.
In RO plants, suspended solids and other particles in the feed water must be removed to reduce fouling of the membranes. Suspended solids are removed with coagulation and filtration. Metals in the feed water are rejected along with the salts by the membranes and are discharged in the brine. With normal concentrations for metals in seawater, the metals present in the brine discharge, though concentrated by the RO process, would not exceed discharge limits. Some distillation plants may also need to remove metals due to potential corrosion problems.
Filter Backwashing, Membrane Cleaning and Storage, Scaling Prevention and Removal, and Pipeline Cleaning
The filters for pre-treatment of feed water at RO plants must be cleaned every few days (backwashed) to clear accumulated sand and solids. The RO membranes must be cleaned approximately four times a year and must be replaced every three to five years. Alkaline cleaners are used to remove organic fouling, and acid cleaners are used to remove scale and other inorganic precipitates. All or a portion of RO plants must be shut down when the membranes are replaced. When RO plants are not used continuously, the RO membranes must be stored in a chemical Disinfection/preservation solution that must be disposed after use. Distillation plants can also be shut down for tube bundle replacement, which is analogous to membrane replacement.
Desalination plant components must be cleaned to reduce scaling-a condition where salts deposit on plant surfaces, such as pipes, tubing or membranes. Scaling is caused by the high salt concentration of sea water and can result in reduced plant efficiency and corrosion of the pipes. In general, scaling increases as temperature increases; thus scaling is of greater concern for distillation plants, since RO plants require lower temperatures to operate. Scaling can be reduced by introducing additives to inhibit crystal growth, reducing temperature and/or salt concentrations, removing scale-forming constituents, or seeding to form particles. Once scales have formed, they can be removed with chemical or mechanical means.
In addition to scaling, both RO and distillation plants’ intake and outfall structures and pipelines can become fouled with naturally occurring organisms or corroded. Structures and pipelines may be cleaned by mechanical means or by applying chemicals or heat. Feed water may also be de-aerated to reduce corrosion.

