Company Information
Ask for more detail from the seller
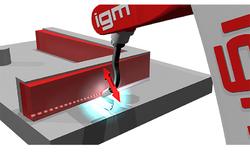
Contact SupplierDuring the welding process arc seam sensing is used to compensate for positional tolerances of the welding seam.
By means of a special software and specifically designed hardware, the "actual" seam position of fillets and V-shaped joints is computed by processing data measured while arc weaving, giving a corresponding shifting of the original programmed point/s to the true seam position.
This arc seam sensing technique can be used with a complete range of welding transfers such as short arc, spray arc and pulsed arc welding - using single or Tandem applications.
By processing data regarding the welding current variation, the robot control system is able to determine the exact welding joint position in 3D during the oscillating welding process. Originally programmed paths are corrected accordingly. The programmed path is corrected on-line in such a way, that the robot follows the joint in all 3 dimensions and keeps the stick out constant throughout the entire welding seam.
Function principle of the arc seam tracking sensorThis online welding seam tracking process is realised by the patented and proven arc controlled seam tracking sensor, type AST.
A built in welding current measuring system via a shunt resistor is permanently measuring the welding arc. The AST sensor card is evaluating the measurement and recording the values at each oscillating point and the middle point. The measurements of the first few oscillating points are recorded and then kept constant throughout the welding joint.
Correction possibilities for the arc seam tracking sensorGenerally several parameters of the used supplies for the robot installation (welding gas purity, welding wire quality, work piece material, different welding parameters, etc.) have an influence on the welding results.
In order to compensate these variations which result in a different arc type, the arc seam tracking sensor AST can be programmed with the following online adjustable settings:
The deviations of the weld groove position ascertained during welding of the root pass will be taken into account for all cover passes. The specific software enables not only to record the deviations with respect to the positions of the programmed steps.
When generating the program, it is also possible to determine the number of intermediate points where off-sets should be memorised and subsequently taken into consideration for welding of the cover passes. By one single step only, it will then be possible to program also long seams which have important deviations in the course of the groove.
Certainly the RCE software enables the programmer to jump between welds to balance the heat input.

